
For example, in a one-tailed test of significance for a normally-distributed variable like the difference of two means, a result which is 1.6448 standard deviations away (1.6448σ) results in a p-value of 0.05.
#TWO MEAN HYPOTHESIS TEST CALCULATOR FULL#
See below for a full proper interpretation of the p-value statistic.Īnother way to think of the p-value is as a more user-friendly expression of how many standard deviations away from the normal a given observation is. Therefore the p-value expresses the probability of committing a type I error: rejecting the null hypothesis if it is in fact true. This equation is used in this p-value calculator and can be visualized as such: calculating a Z-score), X is a random sample (X 1,X 2.X n) from the sampling distribution of the null hypothesis. Where x 0 is the observed data (x 1,x 2.x n), d is a special function (statistic, e.g.

The Student's T-test is recommended mostly for very small sample sizes, e.g. You can use a Z-test (recommended) or a T-test to calculate the observed significance level (p-value statistic).
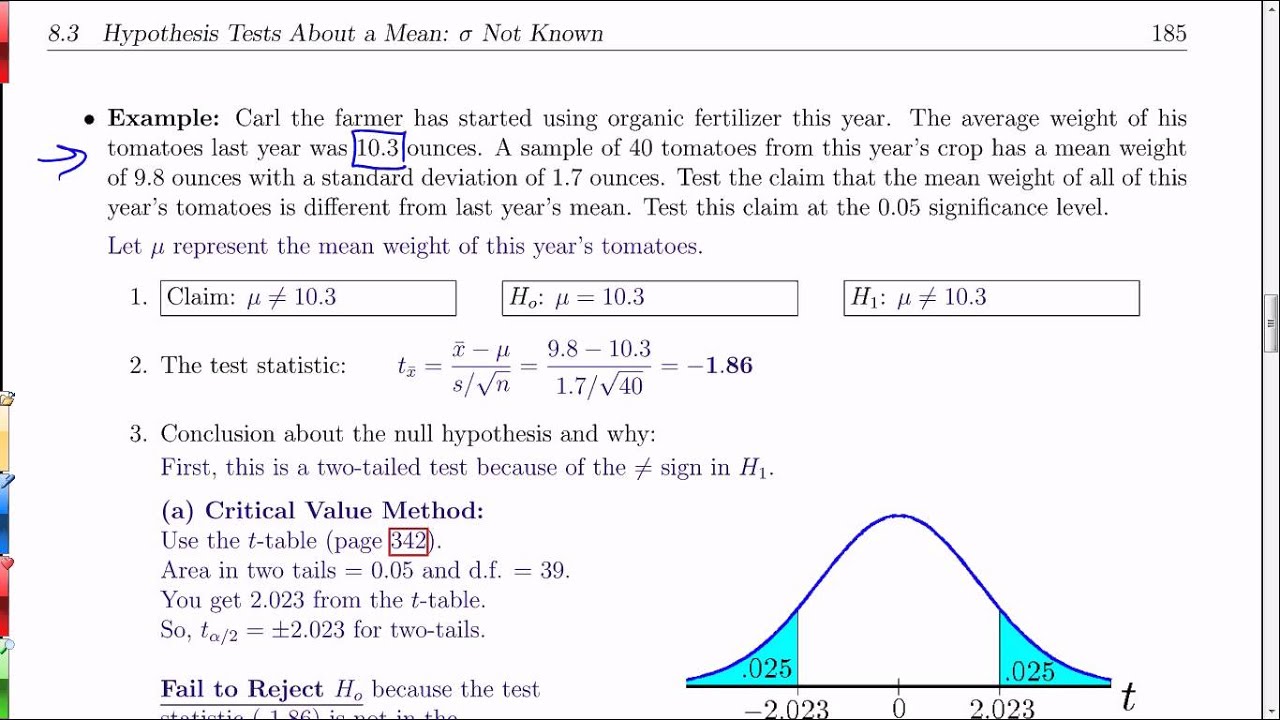
height, weight, speed, time, revenue, etc.). conversion rate or event rate) or difference of two means (continuous data, e.g. This statistical significance calculator allows you to perform a post-hoc statistical evaluation of a set of data when the outcome of interest is difference of two proportions (binomial data, e.g.
#TWO MEAN HYPOTHESIS TEST CALCULATOR HOW TO#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
